Regenerative braking in electric cars is a game-changing technology that not only slows down the vehicle but also recovers kinetic energy to recharge the battery. This smart energy recovery system improves overall efficiency, enhances driving comfort, and extends the range of EVs—especially useful in frequent stop-and-go urban traffic.
In this guide, you’ll learn what regenerative braking is, how it works, its key benefits, and why it’s becoming a must-have feature in modern electric vehicles.
What Is Regenerative Braking in Electric Cars?
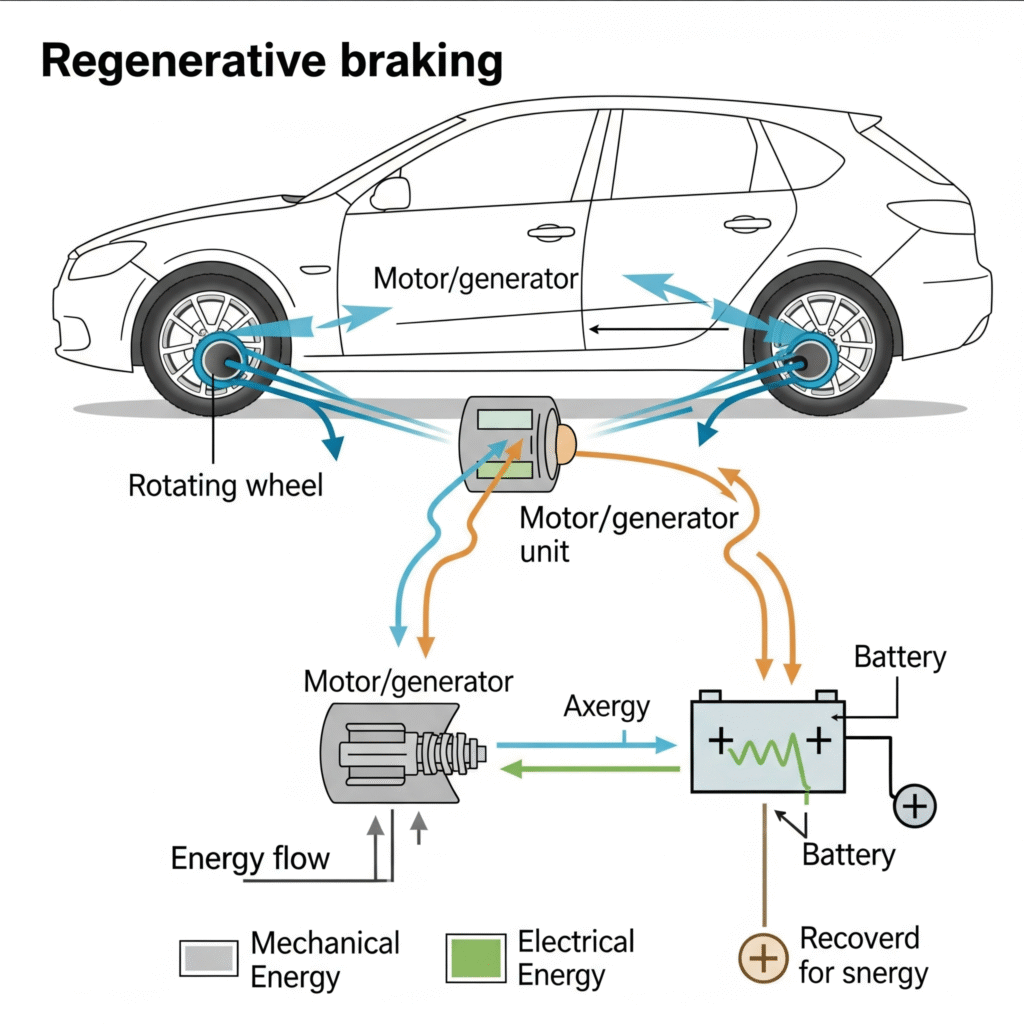
Regenerative braking is a system used in electric and hybrid vehicles to recover energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. Unlike traditional friction brakes that convert kinetic energy into heat, regenerative braking converts this kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then fed back into the EV’s battery.
This process essentially turns the electric motor into a generator during deceleration, enabling the vehicle to recover part of the energy expended during acceleration.
How Regenerative Braking Works in EVs
When an EV driver lifts their foot off the accelerator or presses the brake pedal, the electric motor begins to reverse its role. Instead of consuming electricity, it starts generating electricity by resisting the motion of the wheels. This resistance slows the vehicle down while simultaneously charging the battery.
The recovered energy is stored in the vehicle’s high-voltage battery and can be used again for acceleration, powering accessories, or extending driving range.
Key Components Involved:
- Electric Motor/Generator – Performs dual function based on the vehicle’s motion.
- Power Electronics – Manages the flow of energy back to the battery.
- Battery Management System (BMS) – Controls charging to maintain battery health.
Types of Regenerative Braking
EVs today come with different levels or modes of regenerative braking:
- Coasting Regen – Mild braking when the accelerator is released.
- One-Pedal Driving – Allows full stop of the vehicle just by lifting the foot off the accelerator.
- Adjustable Regen Modes – Found in advanced EVs; allows users to select the intensity of regen.
For example, Tata Nexon EV and Hyundai Kona Electric offer different regenerative modes suited for city or highway driving.
Benefits of Regenerative Braking
1. Improved Energy Efficiency
Regenerative braking can improve overall efficiency by 10–30% depending on the terrain and driving style. This translates into longer driving range and fewer charging stops.
2. Reduced Brake Wear
Since regenerative braking reduces reliance on traditional friction brakes, there is significantly less wear and tear on brake pads, resulting in lower maintenance costs.
3. Better Driving Comfort
In modes like one-pedal driving, regenerative braking makes city driving smoother and less tiring, especially in bumper-to-bumper traffic.
4. Eco-Friendly Technology
By recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted, regenerative braking supports the sustainability mission of EVs. It plays a key role in reducing carbon footprint—discover more reasons why going electric makes sense today
Real-World Examples in Indian EVs
In India, several electric cars and two-wheelers have adopted regenerative braking as a standard feature:
- Tata Nexon EV – Offers multi-level regen that can be adjusted via the infotainment system.
- MG ZS EV – Features three regen modes with noticeable differences in performance.
- Ather 450X – The electric scooter uses regenerative braking seamlessly during deceleration.
- Hyundai Ioniq 5 – Advanced i-Pedal mode offers full one-pedal driving experience.
Limitations of Regenerative Braking
While the technology is impressive, it’s not without its limits:
- Reduced Efficiency at High Speeds – Regen braking is most effective in stop-and-go or city traffic.
- Limited Stopping Power – In emergency situations, friction brakes still play a vital role.
- Battery State of Charge – If the battery is already fully charged, regen braking is disabled to prevent overcharging.
🚗 Quick Comparison Table: Regenerative vs Traditional Braking
| Feature | Traditional Braking | Regenerative Braking |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Recovery | ❌ None | ✅ Yes, converts to electricity |
| Brake Wear | ❌ High | ✅ Low |
| Efficiency Boost | ❌ No impact | ✅ Increases EV range |
| Usage | ✅ All vehicles | ⚠️ EVs/Hybrids only |
| Maintenance Cost | ❌ Higher | ✅ Lower over time |
🔹 Fun Fact
Did You Know?
In Formula E racing, regenerative braking systems are so advanced they allow drivers to recoup up to 30% of energy used during a race lap!
The Future of Regenerative Braking
As EV technology advances, regenerative braking systems are becoming more intelligent. Future systems are expected to integrate AI and machine learning to optimize energy recovery based on driving habits, terrain, and traffic conditions.
Regenerative braking will also play a role in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) energy sharing, where EVs can send stored power back to the grid, making braking energy more meaningful in the larger ecosystem.
Conclusion
Regenerative braking is not just a tech feature—it’s a foundational innovation driving the future of mobility. For Indian EV owners, it offers improved efficiency, smoother city driving, and reduced maintenance costs.
As adoption of EVs grows, understanding systems like regenerative braking will empower drivers to make better use of their vehicle’s full potential.
Whether you’re buying your first EV or just curious about how they work, regenerative braking is a powerful reminder that every slowdown can drive us further.